The Wankel engine is a type of internal combustion engine that was invented by German engineer Felix Wankel in the early 1950s. Unlike traditional reciprocating piston engines, which use a series of cylinders and pistons to convert fuel into mechanical energy, the Wankel engine uses a rotary design that creates power through a continuous combustion cycle.
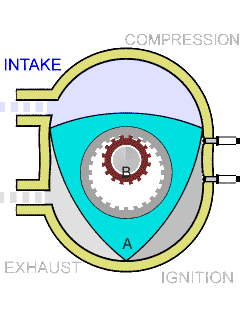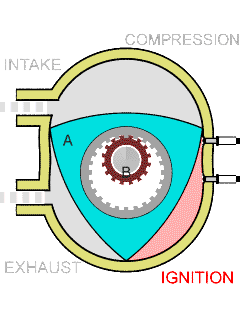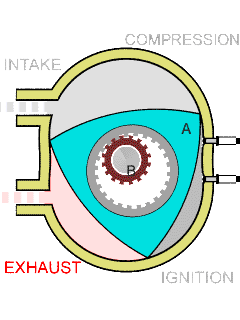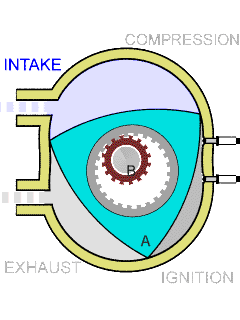
The Wankel engine consists of three basic parts: a rotor, a housing, and an eccentric shaft. The rotor is a triangular or oval-shaped piece of metal that rotates inside the housing, which is a curved, oblong-shaped chamber. The eccentric shaft connects to the rotor and transfers its rotational energy to an output shaft.
The combustion cycle in a Wankel engine is similar to that of a four-stroke engine, but the process is continuous. As the rotor rotates, it passes three separate combustion chambers within the housing. Each chamber is separated by a set of seals, which create a seal between the rotor and the housing.
 |
| The Wankel Engine: A Unique Rotary Design for High Performance Vehicles |
As the rotor rotates, the first chamber sucks in a fuel-air mixture, compresses it, and ignites it with a spark plug. The expanding gases then force the rotor to rotate further, and as it does so, it moves into the second chamber, which is now being filled with fuel-air mixture. This second chamber is now compressing the mixture, and as the rotor moves through it, the mixture is ignited again by another spark plug.
Finally, the third chamber completes the combustion process by allowing the now-exhausted gases to escape out of the engine's exhaust system. At the same time, the third chamber is also preparing to intake a fresh fuel-air mixture from the engine's intake system.
The Wankel engine is known for its high power-to-weight ratio and compact size, making it ideal for use in sports cars and other high-performance vehicles. Because of its rotary design, the engine is also capable of producing a smoother and more balanced power delivery than traditional piston engines.
However, the Wankel engine also has some disadvantages. One of the most significant issues with the design is its fuel economy. Due to the engine's continuous combustion cycle, it has difficulty achieving the same level of fuel efficiency as a traditional piston engine. Additionally, the seals between the rotor and the housing can be prone to wear and tear, which can cause reduced engine performance over time.
Despite these drawbacks, the Wankel engine continues to be used in a variety of applications, including sports cars, motorcycles, and even aircraft. Mazda, in particular, has been a major proponent of the Wankel engine, using it in its RX-series sports cars for several decades.



